Permanent Tissue










Permanent Tissue
Permanent Tissue - The division and differentiation of the cells of meristematic tissues give rise to permanent tissues. Cell division is the formation of two or more daughter cells from one mother cell. A cell has broadly two ‘parts: nucleus and cytoplasm. In cell division both parts divide successively.
Cell differentiation is when developing tissues and organs change from simple to more complex forms to become specialized for specific functions. The cells of permanent tissues lose the capacity to divide and attain a permanent shape, size and function.
Depending on their origin, permanent tissues are of two types—primary and secondary. Primary permanent tissues are derived from apical and intercalary meristems, Secondary permanent tissues are derived from lateral meristems, or cambium cells
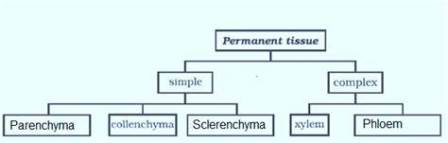
On the basis of their composition, permanent tissues can be simple or complex. Besides these there are special secretory tissues:
Simple permanent tissues consist of similar permanent cells that perform the same function or a similar set of functions. Parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma are three types of simple permanent tissues.
Complex permanent tissues are a group of different types of cells that perform a common function. Xylem and phloem are two types of complex permanent tissues.
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
I have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thA marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thAbout Abhyas metholodology the teachers are very nice and hardworking toward students.The Centre Head Mrs Anu Sethi is also a brilliant teacher.Abhyas has taught me how to overcome problems and has always taken my doubts and suppoeted me.
